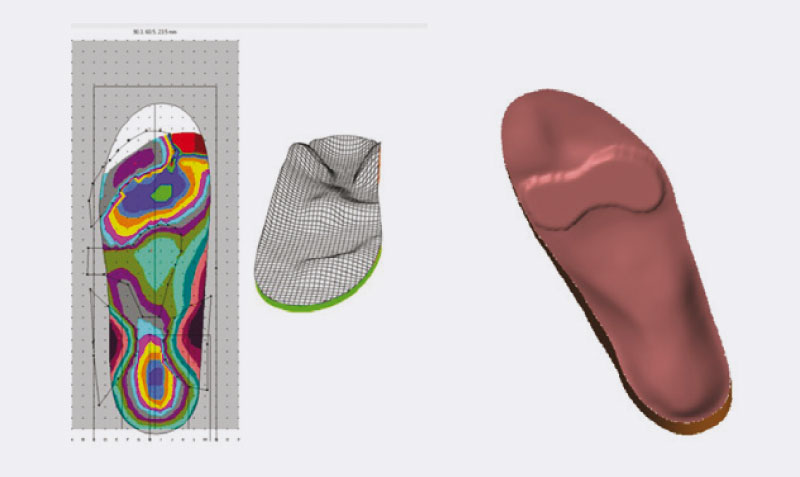
OrthoSenso, Molinari's sensorimotor insole is an insole orthotic product that combines the bio-mechanical concept with the sensorimotor concept concept of orthotic therapy.
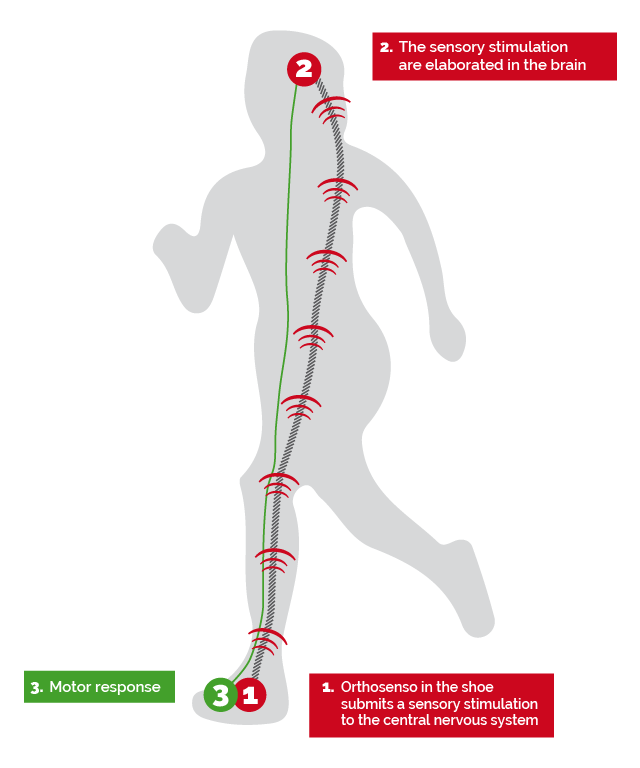
OrthoSenso is a type of orthotic support that does not represent an alternative to the traditional therapeutic action of the insole but it integrates its more physiatrics aspect.
Starting from the three-dimensional shape of the foot obtained from the neutral position of the sub-talar joint, using CAD systems for the design of the sensorimotor insole, the proprioceptive elements are positioned individually by height and intensity and act by reflex in modulating the tone of the various muscle groups affected.
The active and passive elements are reprogrammed periodically depending on the therapeutic purpose of the insole and they are checked in strict cooperation with the physician and physiotherapist.
It is important to highlight that, (remove) in digitalizing the three-dimensional footprint of the foot, the sensory elements, specifically due to the correct set-up in a neutral and axial position of the various areas of the foot, act without encountering any obstacle in carrying out their function because they can be applied to the area and accurate point of the muscle-tendon insertion.
Molinari's sensorimotor insoles can be manufactured as follows:
- with detection of the 3D arch footprint through the Molinari's Amfit and Paracontour system
- through the removal technique starting from an OrthoSenso insole
- through personalization of the insole thanks to the OrthoSenso software database
The sensorimotor elements
They are supports that, through pressure and positioned in the receptor areas of the foot (tendons and muscles), produce muscle responses by reflex.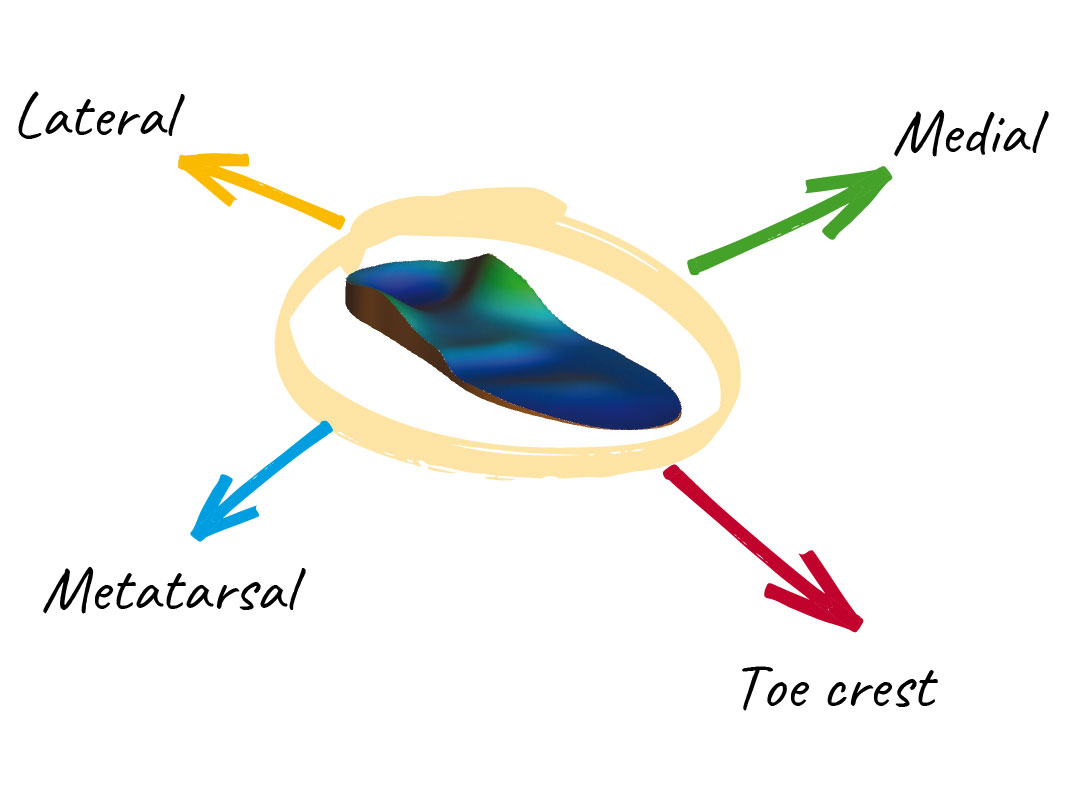
MEDIAL PIN – Activator
The compression along the development line of medial tendons and muscles induces a more intense and earlier activation of these muscles. They are positioned under the Sustentaculum Tali.
Action
The pressure exercised on the tendon places the insertion point and the posterior tibial muscle origin closer to each other. The neural-muscular spindles record a reduction in tension by acting in synergy with the anterior tibial muscle, the muscle reacts early with greater activity.
Effect
- It stabilizes the longitudinal medial arch in the flatfoot and clubfoot
- It counteracts the tendency to overpronation, valgus deviation of the heel, the torsion of the sub-talar joint, and the valgus deviation of the knees.
LATERAL PIN – Inhibitor
Positioned under the peroneal tendons and muscles.
Effect
- It activates the tibiofibular clamp acting in combination with medial stimulation by stabilizing the outer edge of the foot in a clubfoot
- It stabilizes the lateral muscular chains (peroneal, abductory to the iliotibial tract)
- It stabilizes the hip
METATARSAL PIN – Inhibitor
It is positioned just behind the metatarsal heads 2-4.
Action
It stretches the insole band causing a pre-tension of the gastrocnemius, the soleus and the long flexor of the toes.
It increases the longitudinal tension of the neuromuscular spindles, the Golgi's tendinous organs are subjected to strong tension that sends the efferent distraction signals to the muscles.
Effect
- The induced pretension reduces the tone of the calf muscles
- It counteracts the curled retraction of the toes
- It acts on the transverse head of the big toe's adductor muscle
TOE CREST PIN – Inhibitor
It is positioned under the tips of the toes.
Action
It increases the pre-distraction component on the foot short flexor muscles, strengthening the central response upon reduction of calf muscle tension.
Effect
- The uniform contact of the toes to the support surface and the stimulation of the exteroreceptors favor the somatosensory perception
- It helps in modulating the tension of the achilleo-calcaneal-plantar system